Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) prevents the wheels of a vehicle from locking up during braking. It is a safety feature designed to improve vehicle control and reduce the risk of accidents. ABS allows drivers to maintain steering control while braking hard, especially on slippery surfaces. By pulsating the brakes rapidly, it helps prevent wheel lock-up, ensuring the tires maintain traction with the road. This capability significantly reduces the chances of skidding or losing control of the vehicle, thus improving overall safety on the road.
Today’s post will help you learn more about Car ABS in cars and how it works. You will also get to know the significance of the Anti-lock braking system.
Let’s talk about it.
How Does ABS Work in Car?
ABS, or Anti-lock Braking System, is a safety feature in cars that prevents the wheels from locking up during braking, thereby enhancing vehicle control and reducing the risk of accidents. It consists of several components and sensors that work together to achieve its purpose.
The key components of an ABS include wheel speed sensors, an ABS control module, and a hydraulic unit. The wheel speed sensors are located at each wheel and monitor the rotational speed of the wheels. The ABS control module receives signals from these sensors and continuously analyzes them to detect any wheel lock-up or potential skidding.
During normal braking, the ABS operates in conjunction with the vehicle’s brake system. When the driver applies the brakes, the ABS control module receives signals indicating wheel deceleration. If it detects any wheel about to lock up, it activates the hydraulic unit.
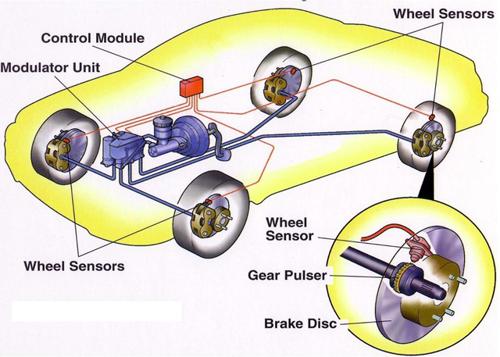
The hydraulic unit, in turn, applies and releases the brakes rapidly, in a pulsating manner. This action helps to maintain traction between the tires and the road, preventing wheel lock-up and allowing the driver to maintain steering control. By modulating brake pressure, ABS assists in brake force distribution, brake assist, traction control, and overall vehicle stability.
In a nutshell, ABS works by continuously monitoring wheel speed and modulating brake pressure to prevent wheel lock-up and skidding during braking. It enhances vehicle safety by providing improved control and stability, especially in emergency braking situations or on slippery surfaces.
ABS Functionality and Features

ABS, or Anti-lock Braking System, offers several important functionalities and features that contribute to vehicle safety and performance. The primary function of ABS is the prevention of wheel lock-up during braking.
By continuously monitoring the rotational speed of each wheel, ABS can detect when a wheel is about to lock up. When this occurs, the system modulates the brake pressure to that particular wheel. Instead of fully applying the brakes, ABS rapidly pulses the brake pressure to maintain the wheel’s rotational speed and prevent it from locking up. This prevents skidding and allows the driver to maintain control and steer the vehicle.
Another crucial aspect of ABS is its contribution to maintaining vehicle stability and maneuverability. By preventing wheel lock-up, ABS ensures that the tires maintain traction with the road surface. This enhances stability during braking, especially on slippery or uneven surfaces. The ability to maintain control over steering while braking increases the driver’s ability to maneuver and avoid obstacles, improving overall safety.
Moreover, ABS improves braking efficiency by optimizing brake force distribution. It modulates the brake pressure individually to each wheel, based on their rotational speed. This allows for optimal braking performance and shorter stopping distances.
In summary, ABS functionality includes preventing wheel lock-up, maintaining vehicle stability, and optimizing braking efficiency through brake modulation. These features contribute to safer braking, improved control, and enhanced maneuverability, ultimately enhancing overall vehicle safety.
Also Read: Why Car Jerks While Driving at Constant Speed: Find Out Now
Common Types of Anti-lock Braking Systems:
There are three main different types of ABS:
- Four-channel, four-sensor ABS: This is the most advanced type of ABS, with a dedicated wheel speed sensor for each wheel. It provides independent control and modulation of the brakes for each wheel, allowing for precise braking and stability control.
- Three-channel, four-sensor ABS: This type of ABS typically has three-wheel speed sensors, with one sensor for each front wheel and a shared sensor for both rear wheels. It offers independent control for each front wheel and a combined control for the rear wheels.
- One-channel, one-sensor ABS: This is the simplest type of ABS, typically found in older vehicles. It has a single-wheel speed sensor, usually located at the rear axle, and controls the braking for all wheels together. While it still provides some benefits over non-ABS systems, it offers less precise control compared to multi-channel systems.
Each type of ABS has its own advantages and limitations, with the four-channel, four-sensor ABS offering the highest level of control and safety.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of ABS:
Proper maintenance and troubleshooting are crucial for the effective functioning of ABS:
- Regular inspection and maintenance of ABS components, such as wheel speed sensors and brake lines, is essential to ensure proper operation.
- Common ABS issues include sensor malfunctions, faulty wiring connections, or hydraulic unit problems. Troubleshooting tips may involve checking sensor connections, cleaning sensors, or inspecting brake fluid levels.
- ABS diagnostic tools, such as OBD-II scanners, can help identify specific ABS issues and retrieve error codes. Professional assistance from mechanics or automotive technicians experienced in ABS systems can provide accurate diagnosis and repairs, especially for complex problems.
Regular maintenance, prompt troubleshooting of common issues, and seeking professional help, when needed, will help ensure the ABS operates optimally, enhancing vehicle safety on the road.
Future Developments and Advancements in ABS:
Future developments in ABS are focused on integration with other advanced safety systems and the evolution of active safety technologies:
- Integration with other safety systems: ABS is being integrated with other safety systems, such as Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Collision Avoidance Systems. This integration allows for more seamless coordination between these systems, enhancing overall vehicle safety.
- Active safety technologies: Advancements in ABS include the incorporation of active safety technologies like forward collision warning, lane departure warning, and adaptive cruise control. These technologies work in tandem with ABS to provide proactive safety measures and improve accident avoidance capabilities.
Additionally, ongoing research and development efforts are aimed at improving ABS sensors, making them more accurate and responsive. These advancements will enhance the ability of ABS to detect wheel lock-up and optimize brake modulation, further improving the effectiveness and performance of ABS systems in future vehicles.
How to check if the car has ABS?
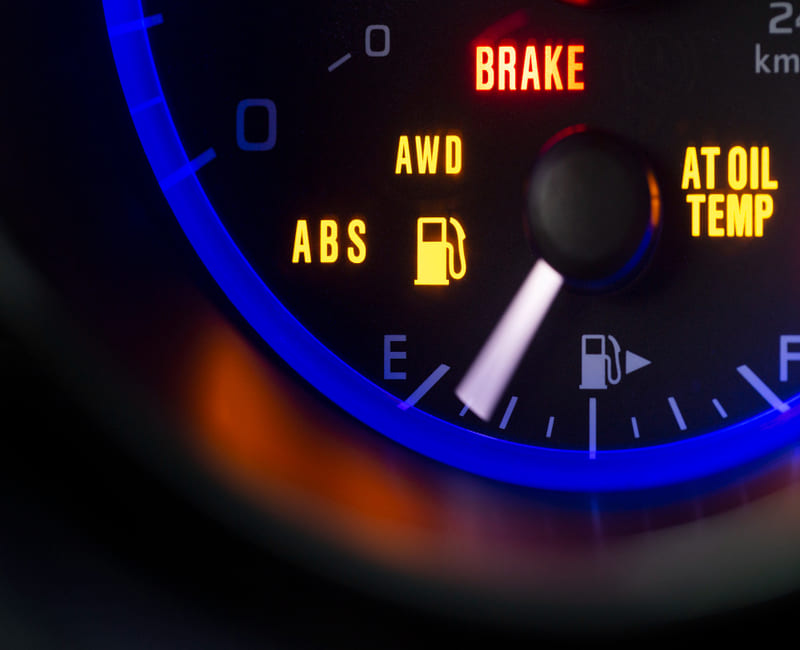

Most of the Cars have ABS warning lights on the dashboard that look like the letters “ABS.” When you start your car, the ABS light will typically illuminate briefly for a system check and then turn off. If you see the ABS light come on and stay on, it indicates your car has a problem with the ABS.
Otherwise, you can also check online by entering your car model and year.
Note: Since 2012, ABS has been a mandatory feature in all cars. So if you own a new car model, there is a high chance that it has ABS.
Final thoughts,
The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is an important safety feature in cars. It prevents wheel lock-up during braking, maintaining vehicle control and stability. In addition, it enhances braking efficiency, maneuverability, and safety, making it an indispensable component for safer and more reliable driving experiences.
Image Credit: Cartrade
FAQs:
1: What are the benefits of using an Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS)?
ABS provides several benefits, including shorter stopping distances, improved steering control during braking & reduced chances of skidding or losing control of the vehicle.
2: Can the Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) fail or require maintenance?
Like any other system in a car, ABS can experience failures or require maintenance. It is crucial to regularly inspect & maintain the ABS components such as sensors, valves & hydraulic systems.
3: Does the Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) work in all driving conditions?
ABS is designed to work effectively in various driving conditions, such as wet, icy, or gravel roads. However, it may be less effective on loose surfaces like deep snow or sand. It is important for drivers to maintain caution and adjust their driving style accordingly in extreme conditions.
